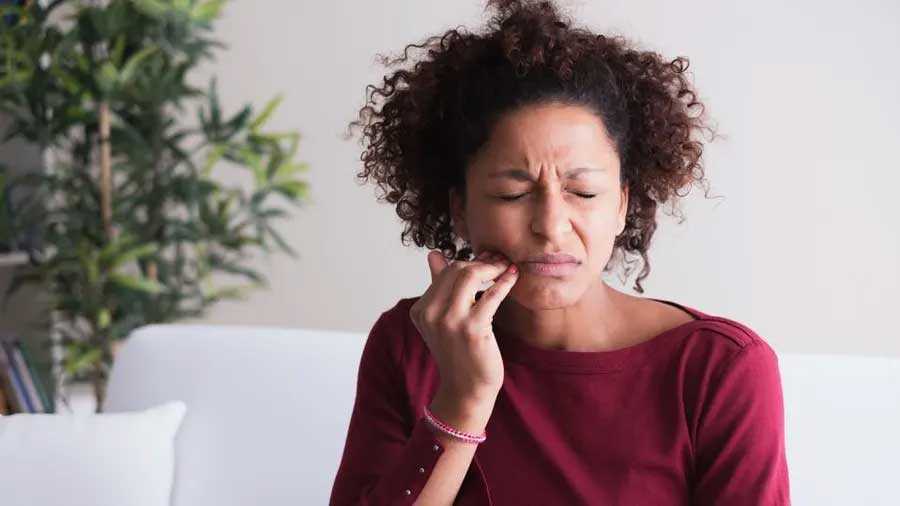
Have you ever taken a bite or sip of something only to find it stings the inside of your mouth? The cause of that sudden pain could be a canker sore—an open wound in your mouth that may appear to be white at first glance.
About one in five people get canker sores regularly[1]. While they typically go away on their own, there are home remedies and dentist prescriptions you can use to speed up the healing process. Learn more about canker sores below, including when to see a doctor about it.
What Is a Canker Sore?
Canker sores, or aphthous ulcers, are shallow, open lesions inside the mouth. They are round or oval in shape and typically red-rimmed and yellow/white in color. Canker sores commonly appear on the insides of the cheeks, on the tongue or gums or inside the lips.
Despite their slightly similar names, canker sores are not the same as cold sores (also known as fever blisters). Cold sores appear most commonly on the lips, but can also emerge on the roof of the mouth. They can be spread by kissing or sharing items, such as utensils; canker sores appear inside the mouth and are not contagious.
Canker sores are also different from potentially precancerous lesions, such as leukoplakia (white lesions) and erythroplakia (any red lesions). Only a biopsy can determine whether the lesion is pre-cancerous—very often these lesions are benign.
Types of Canker Sores
For most of us, a canker sore is a pain no matter what. However, there are slightly different names for canker sore types depending on their size and appearance.
Minor aphthous ulcers are around 2 to 4 millimeters in size. Several can appear in the mouth at once and cause mild pain, according to Fatima Khan, D.D.S., a dentist at Altus Dental in Houston. Minor aphthous ulcers usually go away on their own within one to two weeks.
Major aphthous ulcers are deeper and larger, sometimes reaching 1 centimeter in diameter, says Dr. Khan. These can also appear in the soft palate and throat. Major aphthous ulcers last several weeks to months and can cause fever, pain and difficulty swallowing.
Herpetiform ulcers occur when several small sores combine to make larger, irregularly shaped ulcers. These ulcers look like herpes, but are not caused by the herpes simplex virus.
Recurrent canker sores, or aphthous stomatitis, are when you get canker sores several times a year. Each instance should heal within two weeks, per Beth Goldstein, M.D., a dermatologist and founder of Central Dermatology Center and co-founder of skincare company Modern Ritual based in Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
Canker Sores Symptoms
“Canker sores can begin as a tingling [sensation] in the area of where the sore is about to appear two to three days before it actually appears along with itching and burning,” says Jonelle Anamelechi, D.D.S., owner of Children’s Choice Pediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics in the Washington, D.C. area.
Canker sores are typically painful, and may also itch. They are typically sensitive to spicy, acidic or texturally rough foods.
What Causes a Canker Sore?
A canker sore can be caused by several factors, although it’s tough to pinpoint. According to Dr. Khan, Dr. Anamelechi and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, common causes include:
- Mouth trauma or injury, such as biting your cheek or tongue or cuts from teeth, fillings or dentures
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or menstruation
- Stress
- Deficiency in vitamin B-12, zinc, folic acid or iron
- Sensitivity to chocolate, coffee, strawberries, eggs, nuts, cheese or spicy or acidic foods
- Dental products, like toothpaste, containing sodium lauryl sulfate
- Certain medical conditions, including inflammatory bowel diseases, herpes and HIV/AIDS
Canker sores are more common in women, who experience hormonal changes and are more prone to nutrient deficiencies, says Dr. Khan. “If you are anemic, pay attention to your iron levels and if you are vegan you want to monitor your B12 levels,” she adds.
Canker Sore Diagnosis And Treatments
In most cases, canker sores can be easily diagnosed by a doctor or dentist performing a physical exam and learning more about your medical history. If a sore persists beyond two to three weeks, some doctors may also run blood tests or take a biopsy (removal of tissue for further examination) of the sore to get a better look or idea of what caused the canker sore.
A few reasons you should visit your doctor when it comes to canker sores:
- The sore lasts more than two to three weeks
- The canker sore prevents you from eating or drinking
- Canker sores appear more than two to three times a year
- The sores are large
- The sores occur alongside a fever or atypical canker sore symptoms
You can treat minor canker sores at home with “warm saltwater rinses to decrease inflammation and accelerate the healing process,” recommends Dr. Khan. You can also use milk to coat and soothe the area, says Dr. Anamelechi, as well as avoid any further irritation as best you can.
Per Dr. Khan and Dr. Anamelechi, dentists may prescribe local anesthetics such as topical lidocaine, Orabase or Dexamethasone, a corticosteroid aimed at inflammation.
How to Prevent Canker Sores
Tips for avoiding canker sores from Dr. Khan and Dr. Goldstein include:
- Get enough rest and limit stress
- Avoid triggering foods, such as coffee, chocolate and spicy and acidic foods
- Aim for a well-balanced and nutrient-rich diet
- Brush gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Avoid biting your cheeks
- Avoid toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulfate
Although painful, canker sores are common and most are easily treatable at home. If you can, try to figure out what causes your canker sores so you can better avoid those triggers in the future. If you’re not sure, or if the sores are too painful to deal with, seek help from your doctor or dentist who can prescribe medications to aid the healing process.