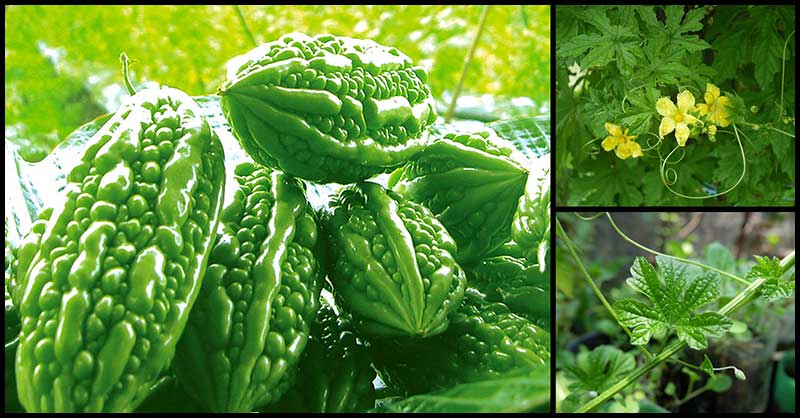
Ampalaya (Bitter Gourd or Bitter Melon) is a climbing vine with tendrils that grow up to 20 centimeters long. Its leaves are heart-shaped, which are 5-10 meters in diameter. This superfood bears fruit that has a ribbed and wrinkled surface that are fleshy green with pointed ends at length and has a bitter taste (1).
Ampalaya And Blood Sugar Management
In terms of nutritional contents, the fruits and leaves of the Ampalaya are reportedly rich in minerals and vitamins, notably iron, calcium, phosphorus, and Vitamin B. It has been considered nature’s answer to diabetes. Today, almost 100 studies have demonstrated the blood sugar lowering effect of this bitter fruit. Dr. A. Raman and Dr. C. Lau, who reviewed over 150 pre-clinical and clinical studies on ampalaya’s anti-diabetes properties and phytochemistry, concluded that “Oral administration of fruit juice or seed powder (of bitter melon) causes a reduction in fasting blood glucose and improves glucose tolerance.” (2)
In the Philippines, several studies were done on ampalaya.
Dr. William Torres, former director of the Bureau of Food and Drugs, came up with this conclusion after reviewing several studies done on ampalaya: “Ampalaya fruits, leaves, seeds and other parts, when used as dry powders, extracts, decoctions, fresh or cooled, have clearly demonstrated hypoglycemic activity.” (4)
Researchers have identified the key compounds present in ampalaya, notably polypeptide-P, a plant insulin found only in the ampalaya. Similar to animal insulin, polypeptide-P lowers elevated blood sugar levels. Dr. Torres maintains that ampalaya when taken regularly, helps to increase glucose tolerance and “potentiate insulin.” (4)
Results of the study conducted by the Philippine Council for Health Research and Development (PCHRD) elevated the ampalaya from a mere nutritional supplement to a real medicine. The study has been certified by the Philippine Institute of Traditional and Alternative Health Care (PITAHC). (3)
“We compared ampalaya leaves with an anti-diabetes drug, and we found out that ampalaya has the same effect on the patient. It means the action of ampalaya on blood sugar is equivalent to the action of the medicine,” Dr. Cirilo Galindez, PITAHC director general, said. (3)
Other Studies Regarding Amplaya’s Ability In Reducing Blood Sugar Levels
Ampalaya has been long been used by indigenous populations around the world to help treat diabetes-related conditions. The fruit contains at least three active substances with anti-diabetic properties, including charantia, which has been confirmed to have a blood glucose-lowering effect, vicine, and an insulin-like compound known as polypeptide-p. These substances either work individually or together to help reduce blood sugar levels. (8)
In a study, Ampalaya is thought to improve the way that sugar is used in our tissues and promote the secretion of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. (5)
Moreover, a 3-month study involving 24 adults with diabetes revealed that taking 2,000 mg of bitter melon every day decreased blood sugar and hemoglobin A1c, a test used to measure blood sugar control over three months. (6)
Regular consumption of Ampalaya was also found to significantly decreased levels of fructosamine, another marker of long-term blood sugar control. (7)
References:
1. https://www.slideshare.net/lopao1024/10-doh-approved-herbal-medicine-pm-zabat
2. https://www.gaiadiscovery.com/food-healthy-living/health-benefits-of-bitter-gourd-or-ampalaya.html
3. https://www.gmanetwork.com/news/news/content/33270/government-recognizes-ampalaya-s-health-benefits
4. https://edgedavao.net/agri-trends/2010/04/26/ampalaya-natural-weapon-against-diseases/
5. https://www.eurekaselect.com/118335/article
6. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/jmf.2017.0114
7. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874110009219?via%3Dihub
8. https://www.diabetes.co.uk/natural-therapies/bitter-melon.html