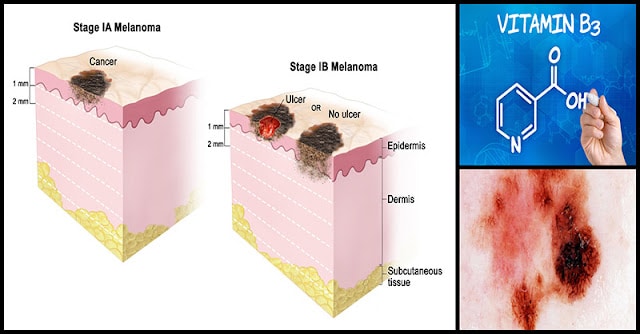
Melanoma is a known deadliest form of skin cancer. While research is still in progress, there is no single drug or combination of drugs that can effectively treat this kind of cancer. Luckily, a study recently conducted had shown that niacin, or vitamin B3, may play a role in the prevention and progression of this disease.
In a review conducted at the University of Sydney and later on published in the journal Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine, scientists concluded that nicotinamide, an active form of vitamin B3, may prevent, melanoma. Furthermore, nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide, was also found to have the ability in enhancing DNA repair in response to UV (ultraviolet) exposure. Melanoma starts in the melanocytes, the skin cells that produce melanin, the protective pigment. Exposure to UV radiation from sunlight damages cell DNA and this is a known risk factor for melanoma.
According to the co-author of the study which was Diona Damian, nicotinamide is the one that re-fills energy stores of keratinocytes, or epidermal skin cells, which was reduced by sun exposure. This enables them to repair DNA damage more efficiently. Additionally, inflammation, which is another risk factor for cancer, can also be reduced by nicotinamide by inhibiting synthesis of inflammatory substances, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-6. The immune suppressive effects of sunlight on the skin can also be lessened with the help of vitamin B3.
Nicotinamide can also overpower vascular mimicry. Vascular mimicry is the one that enables melanoma as well as other tumor cells to form tubular networks that seem to be like normal venous networks.
Another discovery is that nicotinamide impairs the ability of melanoma cells to spread and multiply as well as regulates the activity of sirtuin1, an enzyme involved in the cancer growth. The incidence of precancerous growths that appears in sun-exposed areas in the body can also be reduced by this vitamin.
Another study also showed that nicotinamide can prevent other common types of skin cancer – squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma.
Other health benefits of vitamin B3
Aside from being an essential nutrient for the skin, niacin is also important for every part of the body.
- Lowers the risk of heart disease – cholesterol levels in the body can be regulated by niacin. It also suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress, which harden arteries and block blood flow.
- Supports skin health – Niacin helps in protecting your skin from sun damage.
- Supports mental health – Niacin supplements are often used to treat mood disorders, such as bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety. Patients with depression tend to be deficient in niacin.
- Relieves the symptoms of arthritis – vitamin B3 improves joint mobility and fights inflammation caused by arthritis.
Some of the good sources of niacin are green vegetables, beets, brewer’s yeast, lean meats, fish, nuts, chicken, and eggs.