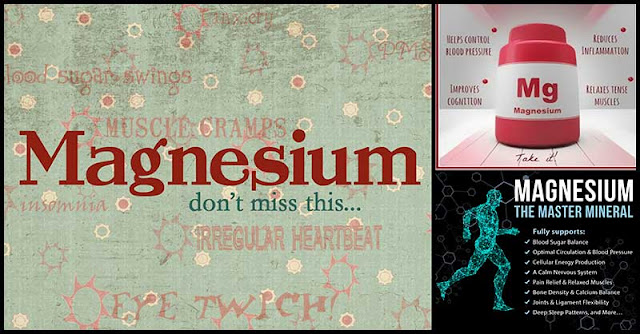
Magnesium is a mineral needed by the body’s regulatory and biochemical systems. It plays a key role in energy production, nerve and muscle function, bone and teeth structure, DNA replication, and RNA and protein synthesis.
Magnesium deficiency, also known as hypomagnesemia, occurs due to inadequate intake or impaired intestinal absorption of magnesium. It is often associated with low potassium and low calcium.
There are certain factors that can increase a person’s risk of developing magnesium deficiency symptoms. These include:
- Continually eating a low-magnesium diet
- Being pregnant and lactating
- Being hospitalized
- Old age
- Taking certain medications, such as antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, bisphosphonates, and diuretics
- Having gastrointestinal disorders such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or regional enteritis
- Having parathyroid disorders and hyperaldosteronism
- Losing excessive amounts of magnesium through urine and sweat resulting from genetic disorders or drinking too much alcohol
- Having type-2 diabetes
Here is the list of early warning signs that could indicate that your body is deficient in magnesium:
Irregular Heartbeat
Insufficient magnesium intake can lead to heart arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat since it can affect all the muscles in the body including the heart muscles. This condition is one of the most serious symptoms of magnesium deficiency. The person may experience chest pain or fainting, shortness in breathing, and lightheadedness. An arrhythmia may increase the risk for complications like strokes and heart attack.
Muscle Cramps Or Tremors
Magnesium deficiency can cause tremors, twitches, and muscle cramps as well as seizures or convulsions in worst case scenario. Since this mineral is needed for optimum muscle function such as to help the muscles relax, lack of sufficient amount can put the body in a state of convulsion.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are stones that are formed out of minerals that are leftover from your urine. The minerals that are responsible for its formation include calcium, oxalate, and phosphorus. With the help of magnesium, kidney stone formation can be stopped. This mineral prevents that binding of calcium with oxalate. It helps the body better manage its calcium, which is essential to stopping those little stones from hurting your urethra.
Depression
According to studies, low levels of magnesium can increase your risk of depression since it has an impact on brain chemistry and hormones.
You are experiencing a major depression if you lose interest or you are at a depressed mood for at least two weeks. You may also have issues about sleeping, concentration, eating, energy, self-image or thoughts of suicide or death.
Ringing In The Ears Or Hearing Loss
Tinnitus is a common symptom of magnesium deficiency. It is described as a ringing in the ears that only the affected person can hear.
Studies revealed that sufficient amounts of magnesium can prevent the formation of free radicals that can lead to hearing loss.
There are foods that are high in magnesium but considering your busy schedule and your day-to-day routine, maybe you don’t always have them in your kitchen. One of the best ways of ensuring you get enough magnesium is by taking a magnesium supplement.
Either way, here is the list of foods you can add in your diet to increase your body’s magnesium levels.
- Nuts, especially almonds, cashews, peanuts
- Seeds (Flax, pumpkin and chia seeds)
- Spinach
- Kale
- Mustard greens
- Black beans
- Edamame
- Peanut butter
- Whole wheat bread
- Avocados
- Bananas
- Potatoes
- Some Fatty Fish (salmon, mackerel and halibut.)