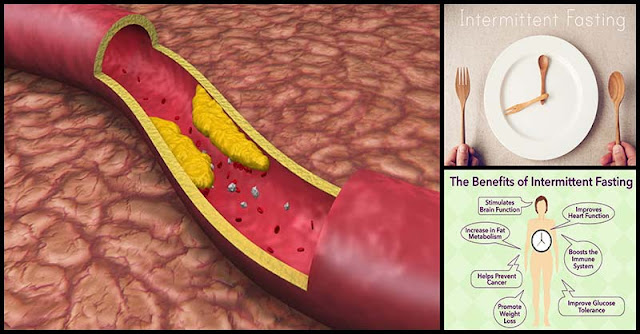
Over the years, fasting has become increasingly popular. It is literally defined as abstaining from food and drink from a specific period of time. People practice fasting for a variety of reasons such as to lose weight, detoxify, cleanse, treat a medical condition, and conform to religious practices.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting involves alternating fasting and eating. This is currently one of the most common health trends nowadays.
Some of the common intermittent fasting methods are as follows:
The 16/8 Method: Fast for 16 hours each day – This method involves fasting every day for 14-16 hours.
Eat-Stop-Eat – This involves a 24-hour fast, either once or twice per week. For instance, you can fast from dinner one day, to dinner the next, this amounts to a 24-hour fast.
The Warrior Diet – This method involves eating small amounts of raw fruits and vegetables during the day and then eating one huge meal at night.
The 5:2 Diet: Fast for 2 days per week – This method involves eating normally 5 days of the week while restricting calories on two days of the week ( 500 calories for women and 600 calories for men).
Alternate-Day Fasting – This means fasting every other day.
Fasting Against Clogged Arteries
According to a study, a person who fasts for one day each month may have a reduced risk of clogged arteries by 40 percent.
Researchers from the Intermountain Medical Center and the University of Utah conducted a survey of 515 people wherein 92 percent of whom were Mormon who suffered from clogged arteries.
The involved people in the study were asked about a number of habits associated with the practice of the Mormon religion which includes observance of a day of rest, church attendance, donation of either time or money to charity, avoidance of caffeine and alcohol, and fasting one day per month.
Based on the data gathered, results revealed that out of the five religious practices, only observance of the monthly fast showed any correlation with heart disease rates. It was found that only 59% of regular fasters developed heart disease as compared to 67% of those who did not fast. Even if the researchers have already adjusted some factors such as weight, age, and health status such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes still the difference between fasters and non-fasters remained.
One of the researchers named Benjamin Horne commented that the relationship between fasting and heart was unclear. He thinks that fasting, along with other factors such as good self-control diet, might also be the reason behind the effect. This is mainly because once the body stops consuming food and sugar, it also stops producing insulin, which can lead to the prevention of the development of the insulin sensitivity associated with Type 2 diabetes, which is a risk factor for heart disease.
Results of this study were presented at a conference of the American Heart Association.
Science-Backed Health Benefits Of Fasting
- Can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body
- Induce various cellular repair processes
- Lower the risk of Type 2 diabetes
- May help prevent cancer
- Good for the brain
- May help prevent Alzheimer’s disease
- Helps you live longer